What is Blow Molding? Let’s Get to Know an Accurate Process in Plastic Manufacturing
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts, such as plastic bottles. In the blow molding process, a hollow tube of plastic, called a parison, is inflated inside a mold to take on the shape of the mold cavity.
This technique is commonly used in the production of a variety of products, from beverage bottles to large containers. The process typically involves heating a plastic tube, inflating it with air, and allowing it to cool inside the mold, giving the plastic its final shape.
Blow molding is divided into several types, including extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding, each offering different benefits depending on the specific application.

Blow Molding Process: Detailed Overview and Types
In the blow molding process, hot polymer is injected into a mold with pressure, taking the shape of the mold. This highly accurate manufacturing method is used for producing hollow plastic parts, but it also has some drawbacks that will be discussed in this article.
Blow molding is done in three main forms: extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch injection blow molding.
How the Blow Molding Process Works:
-
Heating and Preparing the Parison: The process starts by heating the plastic material and creating a preliminary piece called the parison. The parison is a hollow tube with an open end that allows air to pass through.
-
Molding: The parison is then placed inside a mold. Air is blown into it, and the pressure pushes the plastic to expand and cling to the mold’s walls. The air pressure ensures that the material takes the exact shape of the mold cavity.
-
Cooling and Ejection: Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and the molded part is ejected.
Types of Blow Molding:
-
Extrusion Blow Molding: In this type, the parison is formed by extruding a tube of molten plastic. It is then inflated into a mold. This method is commonly used for bottles and other hollow items.
-
Injection Blow Molding: In injection blow molding, the parison is first created by injecting molten plastic into a mold, and then it is inflated inside the mold. This method provides more precision for smaller and more complex shapes.
-
Stretch Injection Blow Molding: This process involves the stretching of a heated parison while air is blown into it. The parison is pulled by a rod and inflated at the same time, ensuring a more uniform wall thickness, and it is commonly used for producing items like beverage bottles.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Blow Molding:
Advantages:
-
High precision and consistency in the molding process.
-
Capable of producing large quantities of hollow plastic parts efficiently.
-
Flexible for different shapes and sizes of plastic products.
Drawbacks:
-
Limited to hollow parts with uniform thickness.
-
Complex molds can be expensive to produce.
-
Potential for material wastage in some cases.
History of Blow Molding
The concept of this method originally came from the idea of blowing into molten glass. Blow molding of plastic materials began in the late 1880s, and between the years of 1930 and 1940, the Hartford Empire company produced items such as Christmas tree decorations.
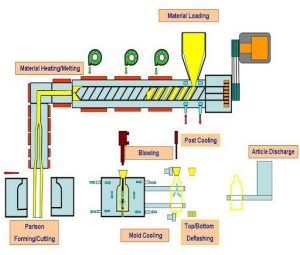
Until the late 1940s, production volumes were limited, and as a result, this method did not spread widely. However, when production volumes increased, this method gained more popularity.
The mechanisms required to create hollow parts had been developed in the past, and after the invention of plastic, glass, which is very fragile, was replaced by plastic in some applications.
The first mass production of plastic bottles took place in 1939 in the United States. Shortly after, Germany began using this process and is now one of the leaders in this field.
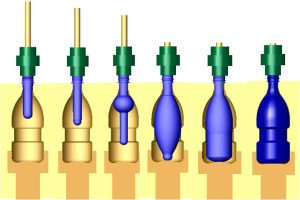
Types of Blow Molding
-
Extrusion Blow Molding
-
Injection Blow Molding
-
Injection Stretch Blow Molding
Extrusion Blow Molding
In this method, the plastic is melted and then extruded into a parison shape. The parison is then placed into a mold, and air is blown into it with pressure. After cooling, the mold opens, and the part is removed.
This process can be performed in two ways: continuous and intermittent. In the continuous process, plastic pellets are extruded continuously, and parisons are formed. They are then placed into molds where air is blown into them under pressure.
In the intermittent process, a thread is created at the top of the parison, followed by injection of the parison, and then air is blown into it. In the continuous blow molding process, the weight of the parison can cause variations in wall thickness, making it challenging to maintain uniform thickness. To address this issue, hydraulic systems quickly remove the parison from the mold to minimize the effects of weight on wall thickness.
Examples of products made with this method include milk bottles, shampoo bottles, and sprayers. The advantages of this method include low tooling costs, high production speed, and the ability to create complex parts. However, the limitations are that it is restricted to hollow parts and has relatively low structural strength.
Injection Blow Molding
This method is used for the mass production of hollow plastic and glass parts. In this process, the initial parison is formed by injection molding and then air is blown into it.

Injection Blow Molding
This method is used less frequently than other blow molding methods and is primarily used for producing disposable containers for pharmaceuticals. In short, the process consists of three steps: injection, blowing, and ejection.
In this process, polymer granules are melted in an extruder and then injected into a mold via a nozzle to form the parison. The parison is then ejected from the mold and placed into another mold, where air is blown into it. After cooling, the mold opens, and the part is removed.
The final part, depending on its size, can have anywhere from 3 to 16 cavities. Usually, 3 ejector pins are used to remove the part from the mold.
Advantages: High precision.
Disadvantages: It is mostly used for small bottle production because controlling the blowing process for larger dimensions is difficult. Also, due to the stretching of the plastic, the parts produced do not have high strength.
Injection Stretch Blow Molding
This method is divided into two types: single-stage and two-stage.
-
Two-Stage Process: In this method, the plastic is first formed into a parison. After cooling, it is reheated to a temperature higher than the glass transition temperature (using infrared radiation), and then placed inside a mold. The parison is stretched while held by a mandrel, and air is blown into it with pressure.
Advantages:
-
Ability to produce large parts.
-
Less design limitation for bottles.
-
The initial parisons can be sold to other factories (unlike in the extrusion blow molding process).
Disadvantages:
-
Requires a large amount of space.
-
High cost.
-
Single-Stage Process: In this process, the parison and the final bottle are produced in the same machine. This reduces costs by up to 25% compared to the two-stage process, where the parisons need to be reheated. In this process, it’s as if molecules are balls with a lot of empty space between them and minimal surface contact. When they are stretched in the vertical direction and then horizontally, the structure becomes cross-linked, increasing the contact surface area and reducing the empty space. This leads to improved final part strength.
Advantages:
-
Since the parison doesn’t cool, it is possible to produce rectangular or non-circular sections with uniform thickness.
Disadvantages:
-
There are limitations in bottle design.