In today’s world, where various industries are seeking to improve the quality, durability, and efficiency of their products, the use of high-quality raw materials plays a key role. One of these widely used raw materials is rubber and rubber compounds, which are widely used in the production of industrial parts, automotive, home appliances, shoes, cable manufacturing, conveyor belts, and many other fields. Mel Industrial and Artistic Tires Company, with years of experience in the supply and wholesale sale of rubber raw materials, is ready to provide the best quality of various rubber compounds, including NBR, SBR, and EPDM, to esteemed manufacturers and industrialists. In the following, we will introduce you to the specifications, features, and important applications of these raw materials so that you can make an informed and confident choice.
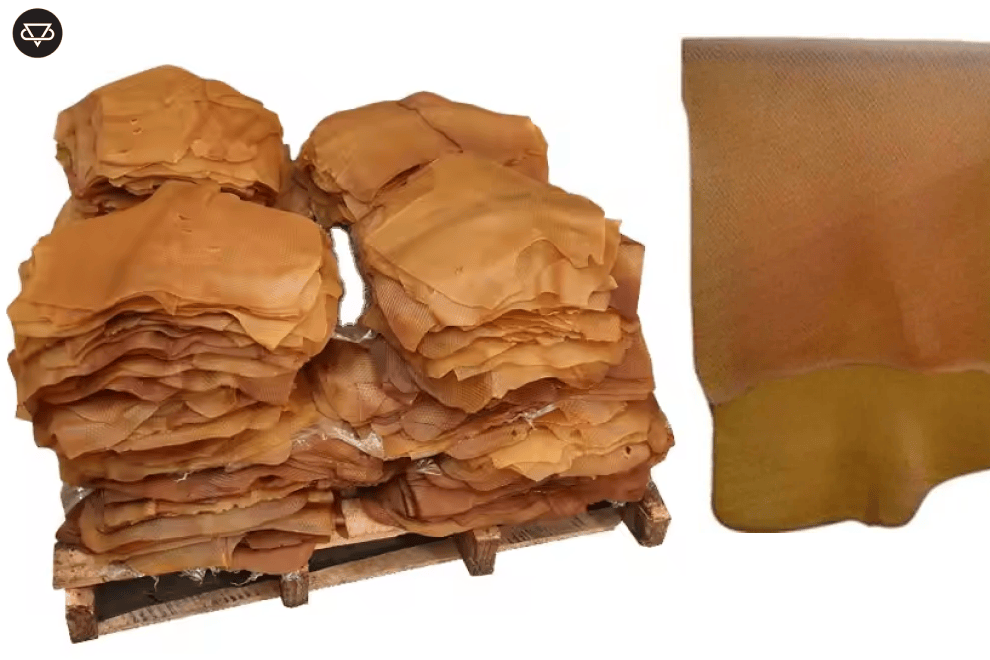

Natural rubber
Natural Rubber, also known by names such as caoutchouc or India rubber, is one of the most important and widely used materials in various industries. This material is used in a wide range of applications with unique properties such as high elasticity, abrasion resistance, and excellent adhesion. It is extracted from the latex of Hevea brasiliensis trees, which grow in the rainforests of Latin America.
Natural rubber production process
The process of producing natural rubber begins with the extraction of latex from the rubber tree. When the bark of the rubber tree is cut, it secretes a milky sap called latex, which contains polyisoprene, organic compounds such as proteins, fatty acids, sugars, and resins. After collection, this latex undergoes various stages of processing.
1. Coagulation:
After the latex is collected, chemicals such as formic acid or acetic acid are used to separate the solid phase from the liquid. These substances cause the rubber particles to separate from the liquid and a solid mass is obtained.
2. Washing & Drying:
The rubber mass obtained after washing is dried to remove impurities. This is done either in the open air or in industrial dryers to get rid of excess moisture and waste materials.
3. Milling & Shaping:
After drying, the rubber is formed into usable sheets or pieces. At this stage, additives such as antioxidants, plasticizers, and processing aids may be added to the rubber to improve its properties.
Properties of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber has many applications in various industries due to its special properties. Due to its polymer structure, this type of rubber exhibits high elasticity, which allows it to return to its original state after being stretched or compressed. Also, its high resistance to wear and friction makes natural rubber a suitable option for the production of tires, industrial machinery parts, and any part that is subject to pressure and wear.
The excellent adhesion of this material provides excellent performance, especially in tire and industrial tire production processes. In addition, natural rubber has good chemical resistance to oils and fuels, which makes it very widely used in the automotive and petroleum industries. In addition, this type of rubber is resistant to temperature changes and has the ability to maintain its stable performance in different temperature conditions.
Applications of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber is widely used in various industries due to its special properties:
Automotive industry:
Natural rubber is especially used in the production of car tires, car accessories (washers) and suspension parts and tires for heavy vehicles. Its elasticity and resistance to wear and pressure make natural rubber an ideal option for this industry.
Footwear industry:
In the production of shoes, especially sports and safety shoes, natural rubber is used as soles and insoles. Durability, adhesion and high comfort are important features that this type of rubber brings to shoemaking.
Medical equipment:
Natural rubber is used in the production of medical equipment such as surgical gloves, tubes and other sensitive equipment. The elasticity and waterproof properties of this type of rubber make it very suitable for this industry.
Electrical Industry:
In the electrical industry, natural rubber is used in the production of cable insulation and other electrical components. Its insulating properties and resistance to heat and pressure make this type of rubber widely used in this industry.
Packaging:
Natural rubber is used in the packaging industry to produce abrasion and impact resistant packaging.

Synthetic rubbers
Synthetic rubber is a type of elastomer that is chemically made from a combination of petroleum-based materials such as monomers. Unlike natural rubber, which is extracted from the latex of the rubber tree, synthetic rubber is produced through a polymerization process in the chemical industry. With its unique properties, this rubber has found wide applications in various industries.
Synthetic rubber raw materials
The main raw materials for the production of synthetic rubber include different types of monomers, which differ depending on the type of synthetic rubber being produced. Some of the most important monomers used in the production of synthetic rubber are:
Styrene: A chemical compound that gives rubber properties such as hardness and heat resistance.
Butadiene: One of the most important monomers in the production of synthetic rubber, giving it elasticity and wear resistance.
Acrylonitrile: This monomer gives rubber good resistance to chemicals, oils, and fuels.
Isobutylene: Used to produce synthetic rubbers with high resistance to harsh weather conditions and chemicals.
These monomers use the polymerization process to form long, chain polymers. Depending on the type of compound and the polymerization process, synthetic rubbers can have different properties.
Synthetic Rubber Production Process
Synthetic rubber production usually involves several main steps:
Polymerization
In this step, various monomers are converted into long polymers in the presence of catalysts and under specific conditions. Depending on the type of synthetic rubber, different polymerization methods are used, such as emulsion, suspension or batch polymerization.
Preparation
After polymerization, the polymers are subjected to various processes such as washing, drying and grinding. This step is necessary to remove impurities and convert the polymer into a form suitable for industrial use.
Shaping
In this step, the synthetic rubber is converted into various forms such as sheets, tubes or molded parts to the desired shape. These parts are then sent to the final stages for the production of functional products.
Vulcanization
The vulcanization process is used to improve the properties of rubber. In this process, rubber is treated with sulfur and heat at high temperatures to create crosslinks in the molecular structure of the polymer. This process gives the rubber strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion, temperature changes, and chemicals.
Types of Synthetic Rubber
Depending on the composition and production process, there are different types of synthetic rubber, each with its own characteristics and applications in different industries. Some of the important types of synthetic rubber are:
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR)
This type of rubber is obtained from a combination of styrene and butadiene and is mostly used in the production of tires and automotive parts. This rubber is one of the most widely used synthetic rubbers due to its good resistance to abrasion and high durability.
Acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR)
This rubber is mostly used in the automotive and oil and gas industries due to its high resistance to oils and fuels. This rubber is used to produce parts that are resistant to chemicals.
Polyisoprene rubber IR
This type of rubber, which is similar to natural rubber, is used especially in the sports tire and medical equipment industries.
Polychloroprene rubber CR
This type of rubber is resistant to weather conditions and chemicals and is usually used in the production of heat-resistant parts and chemicals.
Properties and applications of synthetic rubber
Synthetic rubbers have wide applications in various industries due to their properties such as high resistance to heat, oils, chemicals and abrasion. The most important properties of synthetic rubbers are:
Abrasion resistance: Synthetic rubbers, especially SBR, are used in the production of tires and parts that are exposed to pressure and abrasion due to their anti-abrasion properties.
Chemical resistance: NBR rubbers have good resistance to oils, fuels and chemicals and are therefore used in the automotive and oil and gas industries.
Temperature resistance: Synthetic rubbers such as CR and NBR perform well at high and low temperatures and are used in various weather conditions.
Elasticity: Due to their polymer structure, synthetic rubbers have high elasticity and can withstand tension and pressure.
Applications of synthetic rubber
Synthetic rubbers are used in various industries including automotive, oil and gas, chemical, medical, and aerospace. In the automotive industry, synthetic rubbers are used to produce tires, engine parts, and vehicle equipment. In the oil and gas industry, oil and fuel resistant rubbers are used to produce seals and gaskets.
Synthetic rubbers are also used in the chemical and medical industries as raw materials for the production of pipes, gaskets, and other sensitive parts.
As a result
Natural and synthetic rubbers are among the most important raw materials in various industries, which have many applications due to their unique properties. Natural rubber, with properties such as high elasticity, resistance to abrasion and temperature changes, is obtained from the extraction of latex from rubber trees and is used in industries such as automotive, medical equipment and packaging. On the other hand, synthetic rubbers, which are produced in the polymerization process from petroleum materials, have properties such as greater resistance to heat, chemicals and abrasion and are used in various industries such as automotive, oil and gas, and chemical. Due to technological advances and the need for durable and economical materials, the use of these two types of rubber is expanding and will play a vital role in the future of various industries.